mirror of https://github.com/lumapu/ahoy.git
23 changed files with 751 additions and 402 deletions
@ -1,302 +0,0 @@ |
|||||
## Overview |
|
||||
|
|
||||
On this page, you'll find detailed instructions on how to wire the module of a Wemos D1 mini or ESP32 to the radio module, as well as how to flash it with the latest firmware. This information will enable you to communicate with compatible inverters. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
You find the full [User_Manual here](User_Manual.md) |
|
||||
|
|
||||
## Compatiblity |
|
||||
|
|
||||
The following inverters are currently supported out of the box: |
|
||||
|
|
||||
Hoymiles Inverters |
|
||||
|
|
||||
| Status | Serie | Model | comment | |
|
||||
| ----- | ----- | ------ | ------- | |
|
||||
| ✔️ | MI | 300, 600, 1000/1200/⚠️ 1500 | 4-Channel is not tested yet | |
|
||||
| ✔️ | HM | 300, 350, 400, 600, 700, 800, 1000?, 1200, 1500 | | |
|
||||
| ✔️ | HMS | 350, 500, 800, 1000, 1600, 1800, 2000 | | |
|
||||
| ✔️ | HMT | 1600, 1800, 2250 | | |
|
||||
| ⚠️ | TSUN | [TSOL-M350](https://www.tsun-ess.com/Micro-Inverter/M350-M400), [TSOL-M400](https://www.tsun-ess.com/Micro-Inverter/M350-M400), [TSOL-M800/TSOL-M800(DE)](https://www.tsun-ess.com/Micro-Inverter/M800) | others may work as well (need to be verified). | |
|
||||
|
|
||||
## Table of Contents |
|
||||
|
|
||||
- [Table of Contents](#table-of-contents) |
|
||||
- [Overview](#overview) |
|
||||
- [Compatiblity](#compatiblity) |
|
||||
- [Things needed](#things-needed) |
|
||||
- [There are fake NRF24L01+ Modules out there](#there-are-fake-nrf24l01-modules-out-there) |
|
||||
- [Wiring things up](#wiring-things-up) |
|
||||
- [ESP8266 wiring example on WEMOS D1](#esp8266-wiring-example) |
|
||||
- [Schematic](#schematic) |
|
||||
- [Symbolic view](#symbolic-view) |
|
||||
- [ESP8266 wiring example on 30pin Lolin NodeMCU v3](#esp8266-wiring-example-2) |
|
||||
- [Schematic](#schematic-2) |
|
||||
- [Symbolic view](#symbolic-view-2) |
|
||||
- [ESP32 wiring example](#esp32-wiring-example) |
|
||||
- [Schematic](#schematic-1) |
|
||||
- [Symbolic view](#symbolic-view-1) |
|
||||
- [ESP32 GPIO settings](#esp32-gpio-settings) |
|
||||
- [Flash the Firmware on your Ahoy DTU Hardware](#flash-the-firmware-on-your-ahoy-dtu-hardware) |
|
||||
- [Compiling your own Version](#compiling-your-own-version) |
|
||||
- [Optional Configuration before compilation](#optional-configuration-before-compilation) |
|
||||
- [Using a ready-to-flash binary using nodemcu-pyflasher](#using-a-ready-to-flash-binary-using-nodemcu-pyflasher) |
|
||||
- [Connect to your Ahoy DTU](#connect-to-your-ahoy-dtu) |
|
||||
- [Your Ahoy DTU is very verbose using the Serial Console](#your-ahoy-dtu-is-very-verbose-using-the-serial-console) |
|
||||
- [Connect to the Ahoy DTU Webinterface using your Browser](#connect-to-the-ahoy-dtu-webinterface-using-your-browser) |
|
||||
- [HTTP based Pages](#http-based-pages) |
|
||||
- [MQTT command to set the DTU without webinterface](#mqtt-command-to-set-the-dtu-without-webinterface) |
|
||||
- [Used Libraries](#used-libraries) |
|
||||
- [ToDo](#todo) |
|
||||
|
|
||||
*** |
|
||||
|
|
||||
Solenso Inverters: |
|
||||
|
|
||||
- SOL-H350 |
|
||||
|
|
||||
## Things needed |
|
||||
|
|
||||
If you're interested in building your own AhoyDTU, you'll need a few things to get started. While we've provided a list of recommended boards below, keep in mind that the maker community is constantly developing new and innovative options that we may not have covered in this readme.. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
For optimal performance, we recommend using a Wemos D1 mini or ESP32 along with a NRF24L01+ breakout board as a bare minimum. However, if you have experience working with other ESP boards, any board with at least 4MBytes of ROM may be suitable, depending on your skills. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
Just be sure that the NRF24L01+ module you choose includes the "+" in its name, as we rely on the 250kbps features that are only provided by the plus-variant. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
| **Parts** | **Price** | |
|
||||
| --- | --- | |
|
||||
| D1 ESP8266 Mini WLAN Board Microcontroller | 4,40 Euro | |
|
||||
| NRF24L01+ SMD Modul 2,4 GHz Wi-Fi Funkmodul | 3,45 Euro | |
|
||||
| 100µF / 10V Capacitor Kondensator | 0,15 Euro | |
|
||||
| Jumper Wire Steckbrücken Steckbrett weiblich-weiblich | 2,49 Euro | |
|
||||
| **Total costs** | **10,34 Euro** | |
|
||||
|
|
||||
If you're interested in using our sister project OpenDTU or you want to future-proof your setup, we recommend investing in an ESP32 board that features two CPU cores. As Radio you can also use a NRF24L01+ module with an external antenna. While this option may cost a bit more, it will provide superior performance and ensure compatibility with upcoming developments. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
| **Parts** | **Price** | |
|
||||
| --- | --- | |
|
||||
| ESP32 Dev Board NodeMCU WROOM32 WiFi | 7,90 Euro | |
|
||||
| NRF24L01+ PA LNA SMA mit Antenne Long | 4,50 Euro | |
|
||||
| 100µF / 10V Capacitor Kondensator | 0,15 Euro | |
|
||||
| Jumper Wire Steckbrücken Steckbrett weiblich-weiblich | 2,49 Euro | |
|
||||
| **Total costs** | **14,89 Euro** | |
|
||||
|
|
||||
#### There are fake NRF24L01+ Modules out there |
|
||||
|
|
||||
Watch out, there are some fake NRF24L01+ Modules out there that seem to use rebranded NRF24L01 Chips (without the +).<br/> |
|
||||
An example can be found in [Issue #230](https://github.com/lumapu/ahoy/issues/230).<br/> |
|
||||
You are welcome to add more examples of faked chips. We will add that information here.<br/> |
|
||||
|
|
||||
Some users reported better connection or longer range through more walls when using the |
|
||||
"E01-ML01DP5" EBYTE 2,4 GHz Wireless Modul nRF24L01 + PA + LNA RF Modul, SMA-K Antenna connector, |
|
||||
which has an eye-catching HF cover. But beware: It comes without the antenna! |
|
||||
|
|
||||
In any case you should stabilize the Vcc power by a capacitor and don't exceed the Amplifier Power Level "LOW". |
|
||||
Users reporting good connection over 10m through walls / ceilings with Amplifier Power Level "MIN". |
|
||||
It is not always the bigger the better... |
|
||||
|
|
||||
Power levels "HIGH" and "MAX" are meant to wirings where the nRF24 is supplied by an extra 3.3 Volt regulator. |
|
||||
The bultin regulator on ESP boards has only low reserves in case WiFi and nRF are sending simultaneously. |
|
||||
If you operate additional interfaces like a display, the reserve is again reduced. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
## Wiring things up |
|
||||
|
|
||||
The NRF24L01+ radio module is connected to the standard SPI pins: |
|
||||
|
|
||||
- SCLK (Signal Clock), |
|
||||
- MISO (Master In Slave Out) and |
|
||||
- MOSI (Master Out Slave In) |
|
||||
|
|
||||
*These pins need to be configured in the config.h.* |
|
||||
|
|
||||
Additional, there are 3 pins, which can be set individual: |
|
||||
|
|
||||
- CS (Chip Select), |
|
||||
- CE (Chip Enable) and |
|
||||
- IRQ (Interrupt) |
|
||||
|
|
||||
*These pins can be changed from the /setup URL.* |
|
||||
|
|
||||
#### ESP8266 wiring example on WEMOS D1 |
|
||||
|
|
||||
This is an example wiring using a Wemos D1 mini.<br> |
|
||||
|
|
||||
##### Schematic |
|
||||
|
|
||||
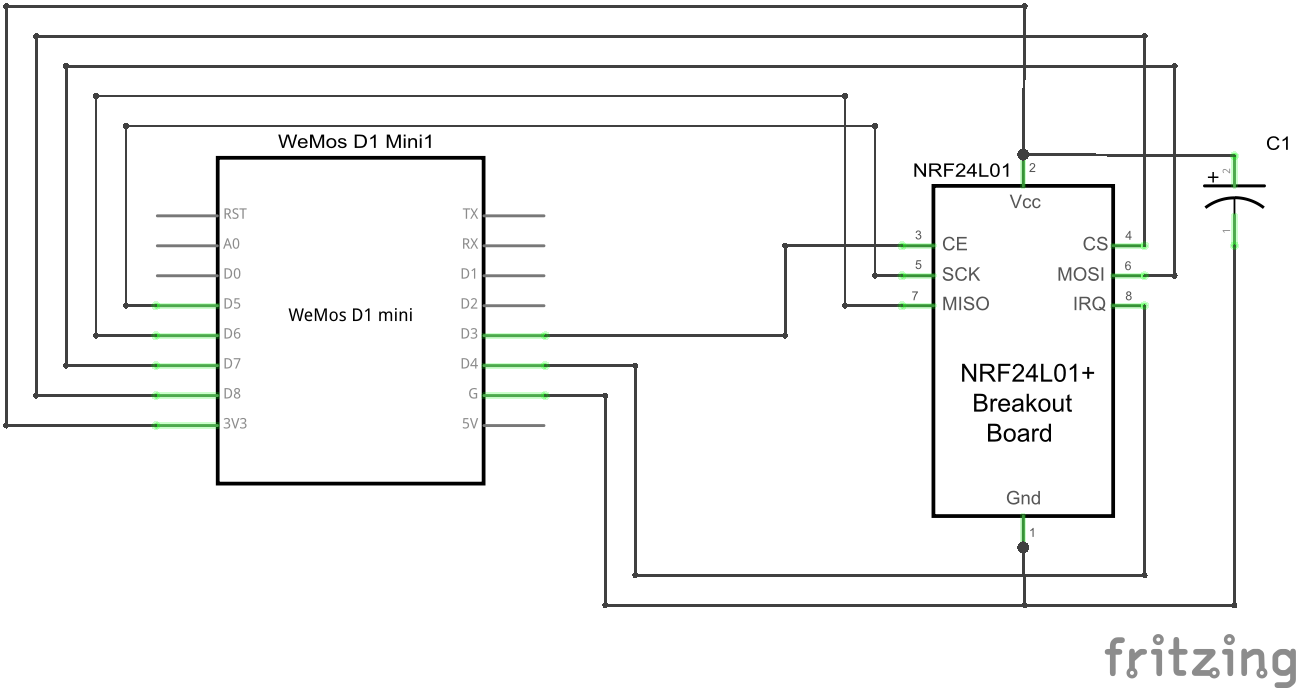 |
|
||||
|
|
||||
##### Symbolic view |
|
||||
|
|
||||
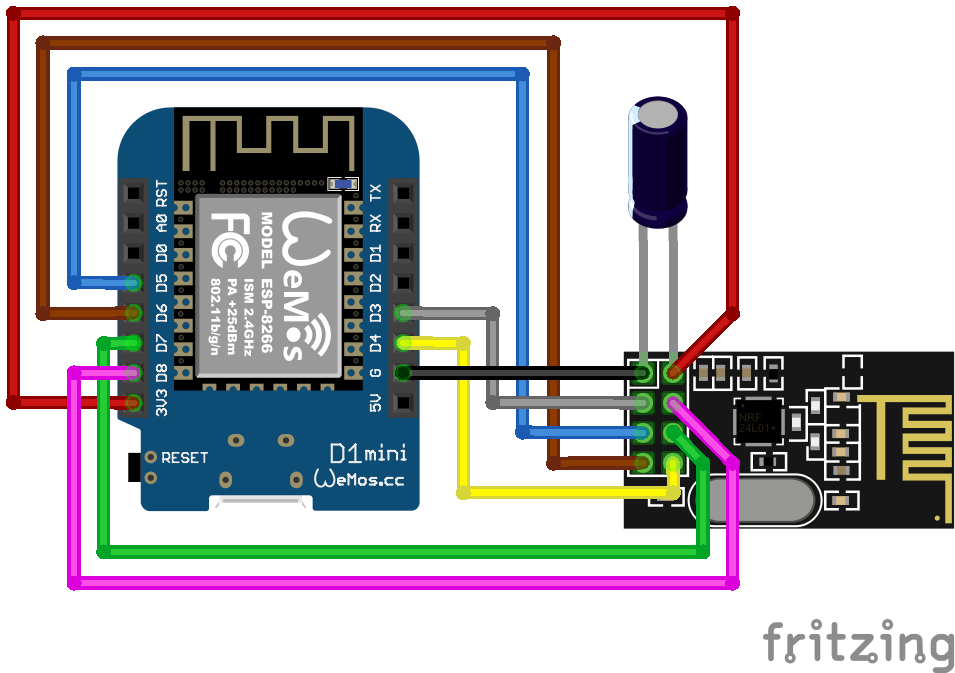 |
|
||||
|
|
||||
#### ESP8266 wiring example on 30pin Lolin NodeMCU v3 |
|
||||
|
|
||||
This is an example wiring using a NodeMCU V3.<br> |
|
||||
|
|
||||
##### Schematic |
|
||||
|
|
||||
 |
|
||||
|
|
||||
##### Symbolic view |
|
||||
|
|
||||
 |
|
||||
|
|
||||
#### ESP32 wiring example |
|
||||
|
|
||||
Example wiring for a 38pin ESP32 module |
|
||||
|
|
||||
##### Schematic |
|
||||
|
|
||||
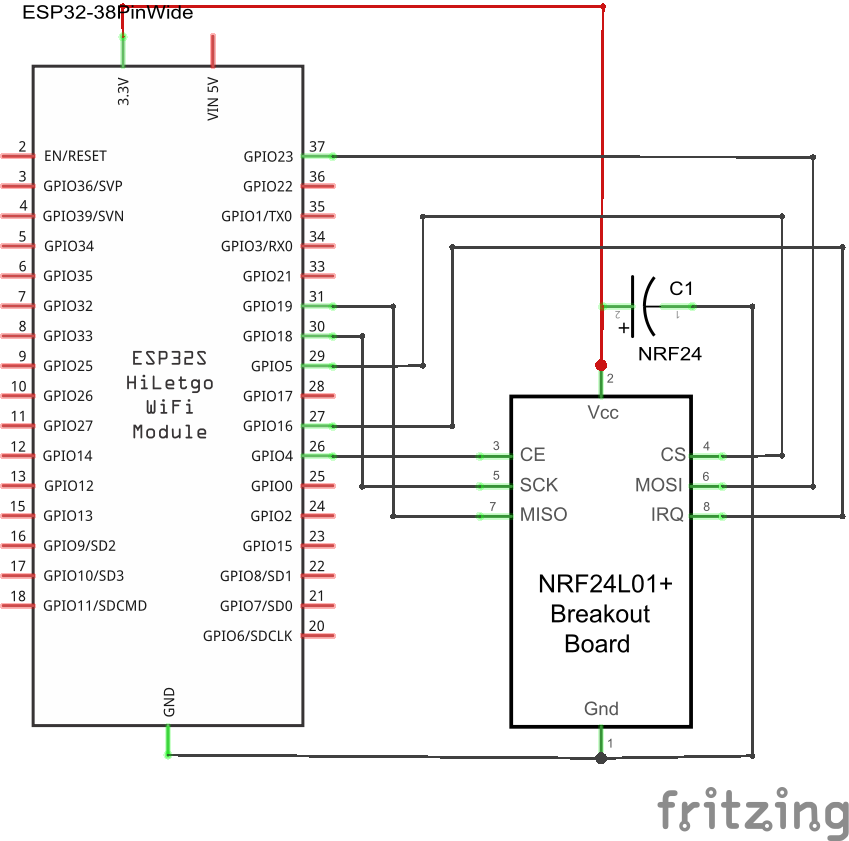 |
|
||||
|
|
||||
##### Symbolic view |
|
||||
|
|
||||
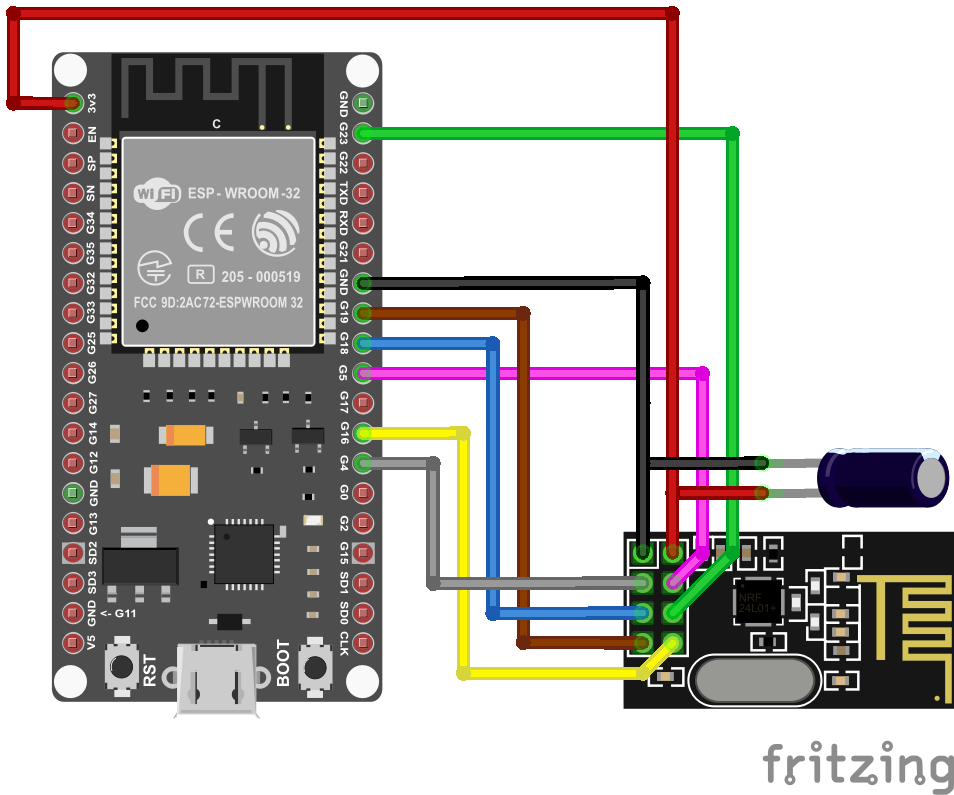 |
|
||||
|
|
||||
##### ESP32 GPIO settings |
|
||||
|
|
||||
CS, CE, IRQ must be set according to how they are wired up. For the diagram above, set the 3 individual GPIOs under the /setup URL as follows: |
|
||||
|
|
||||
``` |
|
||||
CS D1 (GPIO5) |
|
||||
CE D2 (GPIO4) |
|
||||
IRQ D0 (GPIO16 - no IRQ!) |
|
||||
``` |
|
||||
|
|
||||
IMPORTANT: From development version 108/release 0.6.0 onwards, also MISO, MOSI, and SCLK |
|
||||
are configurable. On new installations, their defaults are correct for most ESP32 boards. |
|
||||
These pins cannot be configured for ESP82xx boards, as this chip cannot move them elsewhere. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
If you are upgrading an existing install though, you might see that these pins are set to '0' in the web GUI. |
|
||||
Communication with the NRF module wont work. For upgrading an existing installations, set MISO=19, MOSI=23, SCLK=18 in the settings. |
|
||||
This is the correct default for most ESP32 boards. On ESP82xx, simply saving the settings without changes should suffice. |
|
||||
Save and reboot. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
## Flash the Firmware on your Ahoy DTU Hardware |
|
||||
|
|
||||
Once your Hardware is ready to run, you need to flash the Ahoy DTU Firmware to your Board. |
|
||||
You can either build your own using your own configuration or use one of our pre-compiled generic builds. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
### Flash from your browser (easy) |
|
||||
|
|
||||
The easiest step for you is to flash online. A browser MS Edge or Google Chrome is required. |
|
||||
[Here you go](https://ahoydtu.de/web_install/) |
|
||||
|
|
||||
### Compiling your own Version |
|
||||
|
|
||||
This information suits you if you want to configure and build your own firmware. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
This code comes to you as a **PlatformIO** project and can be compiled using the **PlatformIO** Addon.<br/> |
|
||||
Visual Studio Code, AtomIDE and other IDE's support the PlatformIO Addon.<br/> |
|
||||
If you do not want to compile your own build, you can use one of our ready-to-flash binaries. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
##### Optional Configuration before compilation |
|
||||
|
|
||||
- number of supported inverters (set to 3 by default) `config.h` |
|
||||
- DTU radio id `config.h` (default = 1234567801) |
|
||||
- unformatted list in webbrowser `/livedata` `config.h`, `LIVEDATA_VISUALIZED` |
|
||||
|
|
||||
Alternativly, instead of modifying `config.h`, `config_override_example.h` can be copied to `config_override.h` and customized. |
|
||||
config_override.h is excluded from version control and stays local. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
#### Using a ready-to-flash binary using nodemcu-pyflasher |
|
||||
|
|
||||
This information suits you if you just want to use an easy way. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
1. download the flash-tool [nodemcu-pyflasher](https://github.com/marcelstoer/nodemcu-pyflasher) |
|
||||
2. download latest release bin-file from [ahoy_](https://github.com/grindylow/ahoy/releases) |
|
||||
3. open flash-tool and connect the target device to your computer. |
|
||||
4. Set the correct serial port and select the correct *.bin file |
|
||||
5. click on "Flash NodeMCU" |
|
||||
6. flash the ESP with the compiled firmware using the UART pins or |
|
||||
7. repower the ESP |
|
||||
8. the ESP will start as access point (AP) if there is no network config stored in its eeprom |
|
||||
9. connect to the AP (password: `esp_8266`), you will be forwarded to the setup page |
|
||||
10. configure your WiFi settings, save, repower |
|
||||
11. check your router or serial console for the IP address of the module. You can try ping the configured device name as well. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
Once your Ahoy DTU is running, you can use the Over The Air (OTA) capabilities to update your firmware. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
! ATTENTION: If you update from a very low version to the newest, please make sure to wipe all flash data! |
|
||||
|
|
||||
#### Flashing on Linux with `esptool.py` (ESP32) |
|
||||
1. install [esptool.py](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esptool/en/latest/esp32/) if you haven't already. |
|
||||
2. download and extract the latest release bin-file from [ahoy_](https://github.com/grindylow/ahoy/releases) |
|
||||
3. `cd ahoy_v<XXX> && cp *esp32.bin esp32.bin` |
|
||||
4. Perhaps you need to replace `/dev/ttyUSB0` to match your acual device in the following command. Execute it afterwards: `esptool.py --port /dev/ttyUSB0 --chip esp32 --before default_reset --after hard_reset write_flash --flash_mode dout --flash_freq 40m --flash_size detect 0x1000 bootloader.bin 0x8000 partitions.bin 0x10000 esp32.bin` |
|
||||
5. Unplug and replug your device. |
|
||||
6. Open a serial monitor (e.g. Putty) @ 115200 Baud. You should see some messages regarding wifi. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
## Connect to your Ahoy DTU |
|
||||
|
|
||||
When everything is wired up and the firmware is flashed, it is time to connect to your Ahoy DTU. |
|
||||
|
|
||||
#### Your Ahoy DTU is very verbose using the Serial Console |
|
||||
|
|
||||
When connected to your computer, you can open a Serial Console to obtain additional information.<br/> |
|
||||
This might be useful in case of any troubles that might occur as well as to simply<br/> |
|
||||
obtain information about the converted values which were read out of the inverter(s). |
|
||||
|
|
||||
#### Connect to the Ahoy DTU Webinterface using your Browser |
|
||||
|
|
||||
After you have sucessfully flashed and powered your Ahoy DTU, you can access it via your Browser.<br/> |
|
||||
If your Ahoy DTU was able to log into the configured WiFi Network, it will try to obtain an IP-Address<br/> |
|
||||
from your local DHCP Server (in most cases thats your Router).<br/><br/> |
|
||||
In case it could not connect to your configured Network, it will provide its own WiFi Network that you can<br/> |
|
||||
connect to for furter configuration.<br/> |
|
||||
The WiFi SSID *(the WiFi Name)* and Passwort is configured in the config.h and defaults to the SSID "`AHOY-DTU`" with the Passwort "`esp_8266`".<br/> |
|
||||
The Ahoy DTU will keep that Network open for a certain amount of time (also configurable in the config.h and defaults to 60secs).<br/> |
|
||||
If nothing connects to it and that time runs up, it will retry to connect to the configured network an so on.<br/> |
|
||||
<br/> |
|
||||
If connected to your local Network, you just have to find out the used IP Address or try the default name [http://ahoy-dtu/](http://ahoy-dtu/). In most cases your Router will give you a hint.<br/> |
|
||||
If you connect to the WiFi the Ahoy DTU opens in case it could not connect to any other Network, the IP-Address of your Ahoy DTU is [http://192.168.4.1/](http://192.168.4.1/).<br/> |
|
||||
Just open the IP-Address in your browser.<br/> |
|
||||
<br/> |
|
||||
The webinterface has the following abilities: |
|
||||
|
|
||||
- OTA Update (Over The Air Update) |
|
||||
- Configuration (Wifi, inverter(s), NTP Server, Pinout, MQTT, Amplifier Power Level, Debug) |
|
||||
- visual display of the connected inverters / modules |
|
||||
- some statistics about communication (debug) |
|
||||
|
|
||||
##### HTTP based Pages |
|
||||
|
|
||||
To take control of your Ahoy DTU, you can directly call one of the following sub-pages (e.g. [http://ahoy-dtu/setup](http://ahoy-dtu/setup) or [http://192.168.4.1/setup](http://192.168.4.1/setup) ).<br/> |
|
||||
|
|
||||
| page | use | output | default availability | |
|
||||
| ---- | ------ | ------ | ------ | |
|
||||
| /uptime | displays the uptime uf your Ahoy DTU | 0 Days, 01:37:34; now: 2022-08-21 11:13:53 | yes | |
|
||||
| /reboot | reboots the Ahoy DTU | | yes | |
|
||||
| /erase | erases the EEPROM | | yes | |
|
||||
| /factory | resets to the factory defaults configured in config.h | | yes | |
|
||||
| /setup | opens the setup page | | yes | |
|
||||
| /save | | | yes | |
|
||||
| /cmdstat | show stat from the home page | | yes | |
|
||||
| /visualization | displays the information from your converter | | yes | |
|
||||
| /livedata | displays the live data | | yes | |
|
||||
| /metrics | gets live-data for prometheus | prometheus metrics from the livedata | no - enable via config_override.h | |
|
||||
| /api | gets configuration and live-data in JSON format | json output from the configuration or livedata | yes | |
|
||||
|
|
||||
## MQTT command to set the DTU without webinterface |
|
||||
|
|
||||
[Read here](User_Manual.md) |
|
||||
|
|
||||
## Used Libraries |
|
||||
|
|
||||
| Name | version | License | |
|
||||
| --------------------- | ------- | -------- | |
|
||||
| `ESP8266WiFi` | 1.0 | LGPL-2.1 | |
|
||||
| `DNSServer` | 1.1.1 | LGPL-2.1 | |
|
||||
| `SPI` | 1.0 | LGPL-2.1 | |
|
||||
| `Hash` | 1.0 | LGPL-2.1 | |
|
||||
| `EEPROM` | 1.0 | LGPL-2.1 | |
|
||||
| `ESP Async WebServer` | 1.2.3 | LGPL-3.0 | |
|
||||
| `ESPAsyncTCP` | 1.2.2 | LGPL-3.0 | |
|
||||
| `Time` | 1.6.1 | LGPL-2.1 | |
|
||||
| `RF24` | 1.4.7 | GPL-2.0 | |
|
||||
| `espMqttClient` | 1.4.4 | MIT | |
|
||||
| `ArduinoJson` | 6.21.3 | MIT | |
|
||||
|
|
||||
## ToDo |
|
||||
|
|
||||
[See this post](https://github.com/lumapu/ahoy/issues/142) |
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,302 @@ |
|||||
|
|
||||
|
## Overview |
||||
|
|
||||
|
This page contains detailed instructions on building a module and flashing it with the latest firmware. Following these instructions will allow you to communicate with compatible inverters. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
You find the full [User_Manual here](User_Manual.md) |
||||
|
|
||||
|
## Compatiblity |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Currently, the following inverters are supported: |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Hoymiles Inverters |
||||
|
|
||||
|
| Status | Serie | Model | comment | |
||||
|
| ----- | ----- | ------ | ------- | |
||||
|
| ✔️ | MI | 300, 600, 1000/1200/⚠️ 1500 | 4-Channel is not tested yet | |
||||
|
| ✔️ | HM | 300, 350, 400, 600, 700, 800, 1000?, 1200, 1500 | | |
||||
|
| ✔️ | HMS | 350, 500, 800, 1000, 1600, 1800, 2000 | | |
||||
|
| ✔️ | HMT | 1600, 1800, 2250 | | |
||||
|
| ⚠️ | TSUN | [TSOL-M350](https://www.tsun-ess.com/Micro-Inverter/M350-M400), [TSOL-M400](https://www.tsun-ess.com/Micro-Inverter/M350-M400), [TSOL-M800/TSOL-M800(DE)](https://www.tsun-ess.com/Micro-Inverter/M800) | others may work as well (need to be verified). | |
||||
|
|
||||
|
## Table of Contents |
||||
|
|
||||
|
- [Overview](#overview) |
||||
|
- [Compatiblity](#compatiblity) |
||||
|
- [Things needed](#things-needed) |
||||
|
- [There are fake NRF24L01+ Modules out there](#there-are-fake-nrf24l01-modules-out-there) |
||||
|
- [Wiring things up](#wiring-things-up) |
||||
|
- [ESP8266 wiring example on WEMOS D1](#esp8266-wiring-example) |
||||
|
- [Schematic](#schematic) |
||||
|
- [Symbolic view](#symbolic-view) |
||||
|
- [ESP8266 wiring example on 30pin Lolin NodeMCU v3](#esp8266-wiring-example-2) |
||||
|
- [Schematic](#schematic-2) |
||||
|
- [Symbolic view](#symbolic-view-2) |
||||
|
- [ESP32 wiring example](#esp32-wiring-example) |
||||
|
- [Schematic](#schematic-1) |
||||
|
- [Symbolic view](#symbolic-view-1) |
||||
|
- [ESP32 GPIO settings](#esp32-gpio-settings) |
||||
|
- [Flash the Firmware on your Ahoy DTU Hardware](#flash-the-firmware-on-your-ahoy-dtu-hardware) |
||||
|
- [Compiling your own Version](#compiling-your-own-version) |
||||
|
- [Using a ready-to-flash binary using nodemcu-pyflasher](#using-a-ready-to-flash-binary-using-nodemcu-pyflasher) |
||||
|
- [Connect to your Ahoy DTU](#connect-to-your-ahoy-dtu) |
||||
|
- [Your Ahoy DTU is very verbose using the Serial Console](#your-ahoy-dtu-is-very-verbose-using-the-serial-console) |
||||
|
- [Connect to the Ahoy DTU Webinterface using your Browser](#connect-to-the-ahoy-dtu-webinterface-using-your-browser) |
||||
|
- [HTTP based Pages](#http-based-pages) |
||||
|
- [MQTT command to set the DTU without webinterface](#mqtt-command-to-set-the-dtu-without-webinterface) |
||||
|
- [Used Libraries](#used-libraries) |
||||
|
- [ToDo](#todo) |
||||
|
|
||||
|
*** |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Solenso Inverters: |
||||
|
|
||||
|
- SOL-H350 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
## Things needed |
||||
|
|
||||
|
To build your own AhoyDTU, you only need a few things. Remember that the maker community is always developing new and innovative options that we may not have covered in this readme. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Start with an ESP8266 or ESP32, and combine it with an NRF24L01+ breakout board. Other ESP boards with at least 4MBytes of ROM may also be suitable. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Make sure to choose an NRF24L01+ module that includes the '+' in its name. This is important because we need the 250kbps features that are only available in the plus-variant. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
**Attention**: The NRF24L01+ can only communicate with the MI/HM/TSUN inverter. For the HMS/HMT it is needed to use a CMT2300A! |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
| **Parts** | **Price** | |
||||
|
| --- | --- | |
||||
|
| D1 ESP8266 Mini WLAN Board Microcontroller | 4,40 €| |
||||
|
| *NRF24L01+ SMD Modul 2,4 GHz Wi-Fi Funkmodul (not for HMS/HMT)* | *3,45 €*| |
||||
|
| *CMT2300A 868/915MHz (E49-900M20S)* | *4,59 €* | |
||||
|
| 100µF / 10V Capacitor Kondensator | 0,15 €| |
||||
|
| Jumper Wire Steckbrücken Steckbrett weiblich-weiblich | 2,49 €| |
||||
|
| **Total costs** | **10,34 € / 11,48 €** | |
||||
|
|
||||
|
To future-proof your setup and use our sister project OpenDTU, we recommend investing in an ESP32 board with two CPU cores. Additionally, you can use a NRF24L01+ module with an external antenna as a radio for superior performance and compatibility with upcoming developments. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
| **Parts** | **Price** | |
||||
|
| --- | --- | |
||||
|
| ESP32 Dev Board NodeMCU WROOM32 WiFi | 7,90 €| |
||||
|
| *NRF24L01+ SMD Modul 2,4 GHz Wi-Fi Funkmodul (not for HMS/HMT)* | *3,45 €*| |
||||
|
| *CMT2300A 868/915MHz (E49-900M20S)* | *4,59 €* | |
||||
|
| 100µF / 10V Capacitor Kondensator | 0,15 €| |
||||
|
| Jumper Wire breadboard female-female | 2,49 €| |
||||
|
| **Total costs** | **13,99 € / 15,13 €** | |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### There are fake NRF24L01+ Modules out there |
||||
|
Beware of fake NRF24L01+ modules that use rebranded NRF24L01 chips (without the +). |
||||
|
An example of this can be found in Issue #230 (https://github.com/lumapu/ahoy/issues/230). |
||||
|
If you have any additional examples of fake chips, please share them with us and we will add the information here. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### NRF24L01+ improvements |
||||
|
Users have reported improved connections and longer range through walls when using these modules. |
||||
|
The "E01-ML01DP5" module is a 2.4 GHz wireless module that utilizes the nRF24L01+PA+LNA RF module and features an SMA-K antenna connector. |
||||
|
**The product includes an HF cover, but please note that it does not come with an antenna.** |
||||
|
|
||||
|
To achieve the best results, stabilize the Vcc power by using a capacitor and do not exceed the 'LOW' Amplifier Power Level. |
||||
|
Users have reported good connections over 10m through walls and ceilings when using the Amplifier Power Level 'MIN'. |
||||
|
It's important to remember that bigger is not always better. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
If you are using the NRF24 directly on the ESP board, make sure to set the transmission power to the lowest possible level (this can be adjusted later in the web interface). Using a high transmission power can potentially cause problems. |
||||
|
The ESP board's built-in controller has limited reserves in case both WiFi and nRF are transmitting simultaneously. |
||||
|
If you are using additional interfaces, such as a display, the reserves will be further reduced. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
## Wiring things up |
||||
|
|
||||
|
The NRF24L01+ radio module is connected to the standard SPI pins: |
||||
|
|
||||
|
- SCLK (Signal Clock), |
||||
|
- MISO (Master In Slave Out) and |
||||
|
- MOSI (Master Out Slave In) |
||||
|
|
||||
|
*These pins need to be configured in the config.h.* |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Additional, there are 3 pins, which can be set individual: |
||||
|
|
||||
|
- CS (Chip Select), |
||||
|
- CE (Chip Enable) and |
||||
|
- IRQ (Interrupt) |
||||
|
|
||||
|
*These pins can be changed from the /setup URL.* |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### ESP8266 wiring example on WEMOS D1 |
||||
|
This is an example wiring using a Wemos D1 mini. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
##### Schematic |
||||
|
 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
##### Symbolic view |
||||
|
 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### ESP8266 wiring example on 30pin Lolin NodeMCU v3 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
This is an example wiring using a NodeMCU V3.<br> |
||||
|
|
||||
|
##### Schematic |
||||
|
|
||||
|
 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
##### Symbolic view |
||||
|
|
||||
|
 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### ESP32 wiring example |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Example wiring for a 38pin ESP32 module |
||||
|
|
||||
|
##### Schematic |
||||
|
|
||||
|
 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
##### Symbolic view |
||||
|
|
||||
|
 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
##### ESP32 GPIO settings |
||||
|
|
||||
|
CS, CE, IRQ must be set according to how they are wired up. For the diagram above, set the 3 individual GPIOs under the /setup URL as follows: |
||||
|
|
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
CS D1 (GPIO5) |
||||
|
CE D2 (GPIO4) |
||||
|
IRQ D0 (GPIO16 - no IRQ!) |
||||
|
``` |
||||
|
|
||||
|
**IMPORTANT**: Starting from development version 108/release 0.6.0, MISO, MOSI, and SCLK are also included. |
||||
|
For most ESP32 boards, the default settings are correct on new installations. |
||||
|
However, it is not possible to configure these pins for ESP82xx boards, as they cannot be moved elsewhere. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
If you are upgrading an existing installation, you may notice that the pins are set to '0' in the web GUI, which will prevent communication with the NRF module. |
||||
|
To resolve this, set MISO=19, MOSI=23, SCLK=18 in the settings. |
||||
|
This is the correct default for most ESP32 boards. For ESP82xx, simply saving the settings without changes should suffice. |
||||
|
Save and reboot. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
## Flash the Firmware on your Ahoy DTU Hardware |
||||
|
|
||||
|
After preparing your hardware, you must flash the Ahoy DTU Firmware to your board. |
||||
|
You can either create your own firmware using your configuration or use one of our pre-compiled generic builds. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Are you ready to flash? Then go to next Step here. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### Flash from your browser (easy) |
||||
|
|
||||
|
The easiest step for you is to flash online. A browser MS Edge or Google Chrome is required. |
||||
|
[Here you go](https://ahoydtu.de/web_install/) |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### Compiling your own Version (expert) |
||||
|
This information is for those who wish to configure and build their own firmware. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
The code is provided as a PlatformIO project and can be compiled using the PlatformIO Addon. |
||||
|
The PlatformIO Addon is supported by Visual Studio Code, AtomIDE, and other IDEs. |
||||
|
If you do not wish to compile your own build, you can use one of our pre-compiled binaries. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### Using a ready-to-flash binary using nodemcu-pyflasher |
||||
|
|
||||
|
This information suits you if you just want to use an easy way. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
1. download the flash-tool [nodemcu-pyflasher](https://github.com/marcelstoer/nodemcu-pyflasher) |
||||
|
2. download latest release bin-file from [ahoy_](https://github.com/grindylow/ahoy/releases) |
||||
|
3. open flash-tool and connect the target device to your computer. |
||||
|
4. Set the correct serial port and select the correct *.bin file |
||||
|
5. click on "Flash NodeMCU" |
||||
|
6. flash the ESP with the compiled firmware using the UART pins or |
||||
|
7. repower the ESP |
||||
|
8. the ESP will start as access point (AP) if there is no network config stored in its eeprom |
||||
|
9. connect to the AP (password: `esp_8266`), you will be forwarded to the setup page |
||||
|
10. configure your WiFi settings, save, repower |
||||
|
11. check your router or serial console for the IP address of the module. You can try ping the configured device name as well. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Once your Ahoy DTU is running, you can use the Over The Air (OTA) capabilities to update your firmware. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
**! ATTENTION: If you update from a very low version to the newest, please make sure to wipe all flash data!** |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### Flashing on Linux with `esptool.py` (ESP32) |
||||
|
1. install [esptool.py](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esptool/en/latest/esp32/) if you haven't already. |
||||
|
2. download and extract the latest release bin-file from [ahoy_](https://github.com/grindylow/ahoy/releases) |
||||
|
3. `cd ahoy_v<XXX> && cp *esp32.bin esp32.bin` |
||||
|
4. Perhaps you need to replace `/dev/ttyUSB0` to match your acual device in the following command. Execute it afterwards: `esptool.py --port /dev/ttyUSB0 --chip esp32 --before default_reset --after hard_reset write_flash --flash_mode dout --flash_freq 40m --flash_size detect 0x1000 bootloader.bin 0x8000 partitions.bin 0x10000 esp32.bin` |
||||
|
5. Unplug and replug your device. |
||||
|
6. Open a serial monitor (e.g. Putty) @ 115200 Baud. You should see some messages regarding wifi. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
## Connect to your Ahoy DTU |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Once everything is wired and the firmware is flashed, it is time to connect to your Ahoy DTU. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### Your Ahoy DTU is very verbose using the Serial Console |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Once connected to your computer, you can open a serial console to get additional information. |
||||
|
This can be useful for troubleshooting, as well as simply to get |
||||
|
information about the converted values read from the inverter(s). |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### Connect to the Ahoy DTU Webinterface using your Browser |
||||
|
|
||||
|
After you have successfully flashed and powered up your Ahoy DTU, you can access it from your browser.<br/> |
||||
|
If your Ahoy DTU was able to log on to the configured WiFi network, it will try to obtain an IP address from your local DHCP server (in most cases this is your router). |
||||
|
|
||||
|
If it cannot connect to your configured network, it will provide its own WiFi network that you can |
||||
|
to for further configuration. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
The WiFi SSID *(the WiFi name)* and password are pre-configured and are set to SSID "`AHOY-DTU`" and password "`esp_8266`" by default. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
The Ahoy DTU will keep this network open for a certain amount of time (default is 60sec). |
||||
|
If nothing connects to it and the time expires, it will retry to connect to the configured network, and so on. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
If you are connected to your local network, just find out the IP address used or try the default name [http://ahoy-dtu/](http://ahoy-dtu/). |
||||
|
In most cases, your router will give you a hint. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
If you connect to the WiFi the Ahoy DTU opens in case it could not connect to any other Network, the IP-Address of your Ahoy DTU is [http://192.168.4.1/](http://192.168.4.1/). |
||||
|
Just open the IP-Address in your browser. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
The web interface has the following capabilities: |
||||
|
|
||||
|
- Live data (values updated every 5 seconds) |
||||
|
Click on the title/name/alarm for more actions. |
||||
|
- Webserial (Debug) |
||||
|
- Settings (System Config, Network, Protection, Inverter, NTP Server, Sunrise/Sunset, MQTT, Display Config) |
||||
|
- Update (Over The Air Update) |
||||
|
- System (status about the modules) |
||||
|
|
||||
|
##### HTTP based Pages |
||||
|
|
||||
|
To take control of your Ahoy DTU, you can directly call one of the following sub-pages (e.g. [http://ahoy-dtu/setup](http://ahoy-dtu/setup) or [http://192.168.4.1/setup](http://192.168.4.1/setup) ). |
||||
|
|
||||
|
| page | use | output | default availability | |
||||
|
| ---- | ------ | ------ | ------ | |
||||
|
| /logout| logout the user from webinterface | | yes | |
||||
|
| /reboot | reboots the Ahoy DTU | | yes | |
||||
|
| /system| show system inforamtion | | yes | |
||||
|
| /live | displays the live data | | yes | |
||||
|
| /save | | | yes | |
||||
|
| /erase | erases the EEPROM | | yes | |
||||
|
| /factory | resets to the factory defaults configured in config.h | | yes | |
||||
|
| /setup | opens the setup page | | yes | |
||||
|
| /metrics | gets live-data for prometheus | prometheus metrics from the livedata | no - enable via config_override.h | |
||||
|
| /api | gets configuration and live-data in JSON format | json output from the configuration or livedata | yes | |
||||
|
|
||||
|
## MQTT command to set the DTU without webinterface |
||||
|
|
||||
|
[Read here](User_Manual.md) |
||||
|
|
||||
|
## Used Libraries |
||||
|
|
||||
|
| Name | version | License | |
||||
|
| --------------------- | ------- | -------- | |
||||
|
| `ESP8266WiFi` | 1.0 | LGPL-2.1 | |
||||
|
| `DNSServer` | 1.1.1 | LGPL-2.1 | |
||||
|
| `SPI` | 1.0 | LGPL-2.1 | |
||||
|
| `Hash` | 1.0 | LGPL-2.1 | |
||||
|
| `EEPROM` | 1.0 | LGPL-2.1 | |
||||
|
| `ESPAsyncWebServer` | 1.2.3 | LGPL-3.0 | |
||||
|
| [ESPAsyncTCP](https://github.com/me-no-dev/ESPAsyncTCP) | 1.2.2 | [LGPL-3.0 license](https://github.com/me-no-dev/ESPAsyncTCP#LGPL-3.0-1-ov-file) | |
||||
|
| [Time](https://github.com/PaulStoffregen/Time) | 1.6.1 | ? | |
||||
|
| [RF24](https://github.com/nRF24/RF24) | 1.4.8 | [GPL-2.0 license](https://github.com/nRF24/RF24#GPL-2.0-1-ov-file) | |
||||
|
| [espMqttClient](https://github.com/bertmelis/espMqttClient) | ? | [MIT license](https://github.com/bertmelis/espMqttClient#MIT-1-ov-file) | |
||||
|
| [ArduinoJson](https://github.com/bblanchon/ArduinoJson) | 6.21.3 | [MIT license](https://github.com/bblanchon/ArduinoJson#MIT-1-ov-file)| |
||||
|
| [GxEPD2](https://github.com/ZinggJM/GxEPD2) | 1.5.2 | [GPL-3.0 license](https://github.com/ZinggJM/GxEPD2#GPL-3.0-1-ov-file)| |
||||
|
| [U8g2_Arduino](https://registry.platformio.org/libraries/olikraus/U8g2) | [2.35.9](https://registry.platformio.org/libraries/olikraus/U8g2/versions) | [BSD-2-Clause](https://spdx.org/licenses/BSD-2-Clause.html) | |
||||
|
|
||||
|
## ToDo |
||||
|
|
||||
|
[See this post](https://github.com/lumapu/ahoy/issues/142) |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,65 @@ |
|||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
## Ahoy configuration |
||||
|
|
||||
|
So far we have built our own DTU, written a program on it and put it into operation. |
||||
|
But how do I get my data from the inverter? |
||||
|
|
||||
|
To do this, we need to configure the DTU. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
The following steps are required: |
||||
|
1. Set the pinning to communicate with the radio module. |
||||
|
2. Check if Ahoy has a current time |
||||
|
3. Set inverter data |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 1.) Set the pinning |
||||
|
Once you are in the web interface, you will find the "System Config" sub-item in the Setup area (left). |
||||
|
|
||||
|
This is where you tell the ESP how you connected the radio module. |
||||
|
Note the schematics you saw earlier. - If you haven't noticed them yet, here's another table of connections. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### OpenDTU Fusion (ESP32-S3) |
||||
|
| NRF24 Pin | ESP Pin| |
||||
|
|---------| --------| |
||||
|
| CS (4) | GPIO37 |
||||
|
| CE (3)| GPIO38 |
||||
|
| IRQ (8) | GPIO47 |
||||
|
| SCLK (5)| GPIO36 |
||||
|
| MOSI (6)| GPIO35 |
||||
|
| MISO (7)| GPIO48 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
| CMT2300A | Pin | |
||||
|
|---------| --------| |
||||
|
| CMT| Enabled | |
||||
|
| SCLK| GPIO6 |
||||
|
| SDIO| GPIO5 |
||||
|
| CSB| GPIO4 |
||||
|
| FCSB| GPIO21 |
||||
|
| GPIO3| GPIO8 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 2.) Set current time (normal skip this step) |
||||
|
Ahoy needs a current date and time to talk to the inverter. |
||||
|
It works without, but it is recommended to include a time. This allows you to analyze information from the inverter in more detail. |
||||
|
Normally, a date/time should be automatically retrieved from the NTP server. However, it may happen that the firewall of some routers does not allow this. |
||||
|
In the section "Settings -> NTP Server" you can also get the time from your own computer. Or set up your own NTP server. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
### 3.) Set inverter data |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### add new inverter |
||||
|
Now it's time to place the inverter. This is necessary because it is not the inverter that speaks first, but the DTU (Ahoy). |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Each inverter has its own S.Nr. This also serves as an identity for communication between the DTU and the inverter. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
The S.Nr is a 12-digit number. You can look it up [here (german)](https://github.com/lumapu/ahoy/wiki/Hardware#wie-ist-die-serien-nummer-der-inverter-aufgebaut) for more information. |
||||
|
#### set pv-modules (not necessary) |
||||
|
Click on "Add Inverter" and enter the S.No. and a name. Please keep the name short! |
||||
|
In the upper tab "Inputs" you can enter the data of the solar modules. These are only used directly in Ahoy for calculation and have no influence on the inverter. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### set radio parameter (not necessary, only for EU) |
||||
|
In the next tab "Radio" you can adjust the power and other parameters if necessary. However, these should be left as default (EU only). |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#### advanced options (not necessary) |
||||
|
In the "Advanced" section, you can customize more settings. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
# Done - Now check the live site |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,99 @@ |
|||||
|
#include <algorithm> |
||||
|
#include "syslog.h" |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#ifdef ENABLE_SYSLOG |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#define SYSLOG_MAX_PACKET_SIZE 256 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
void DbgSyslog::setup(settings_t *config) { |
||||
|
mConfig = config; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
// Syslog callback overrides web-serial callback
|
||||
|
registerDebugCb(std::bind(&DbgSyslog::syslogCb, this, std::placeholders::_1)); // dbg.h
|
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
void DbgSyslog::syslogCb (String msg) |
||||
|
{ |
||||
|
if (!mSyslogIP.isSet()) { |
||||
|
// use WiFi.hostByName to DNS lookup for IPAddress of syslog server
|
||||
|
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECTED) { |
||||
|
WiFi.hostByName(SYSLOG_HOST,mSyslogIP); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
if (!mSyslogIP.isSet()) { |
||||
|
return; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
uint16_t msgLength = msg.length(); |
||||
|
uint16_t msgPos = 0; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
do { |
||||
|
uint16_t charsToCopy = std::min(msgLength-msgPos,SYSLOG_BUF_SIZE - mSyslogBufFill); |
||||
|
|
||||
|
while (charsToCopy > 0) { |
||||
|
mSyslogBuffer[mSyslogBufFill] = msg[msgPos]; |
||||
|
msgPos++; |
||||
|
mSyslogBufFill++; |
||||
|
charsToCopy--; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
mSyslogBuffer[mSyslogBufFill] = '\0'; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
bool isBufferFull = (mSyslogBufFill == SYSLOG_BUF_SIZE); |
||||
|
bool isEolFound = false; |
||||
|
if (mSyslogBufFill >= 2) { |
||||
|
isEolFound = (mSyslogBuffer[mSyslogBufFill-2] == '\r' && mSyslogBuffer[mSyslogBufFill-1] == '\n'); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
// Get severity from input message
|
||||
|
if (msgLength >= 2) { |
||||
|
if (':' == msg[1]) { |
||||
|
switch(msg[0]) { |
||||
|
case 'E': mSyslogSeverity = PRI_ERROR; break; |
||||
|
case 'W': mSyslogSeverity = PRI_WARNING; break; |
||||
|
case 'I': mSyslogSeverity = PRI_INFO; break; |
||||
|
case 'D': mSyslogSeverity = PRI_DEBUG; break; |
||||
|
default: mSyslogSeverity = PRI_NOTICE; break; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
if (isBufferFull || isEolFound) { |
||||
|
// Send mSyslogBuffer in chunks because mSyslogBuffer is larger than syslog packet size
|
||||
|
int packetStart = 0; |
||||
|
int packetSize = 122; // syslog payload depends also on hostname and app
|
||||
|
char saveChar; |
||||
|
if (isEolFound) { |
||||
|
mSyslogBuffer[mSyslogBufFill-2]=0; // skip \r\n
|
||||
|
} |
||||
|
while(packetStart < mSyslogBufFill) { |
||||
|
saveChar = mSyslogBuffer[packetStart+packetSize]; |
||||
|
mSyslogBuffer[packetStart+packetSize] = 0; |
||||
|
log(mConfig->sys.deviceName,SYSLOG_FACILITY, mSyslogSeverity, &mSyslogBuffer[packetStart]); |
||||
|
mSyslogBuffer[packetStart+packetSize] = saveChar; |
||||
|
packetStart += packetSize; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
mSyslogBufFill = 0; |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
} while (msgPos < msgLength); // Message not completely processed
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
void DbgSyslog::log(const char *hostname, uint8_t facility, uint8_t severity, char* msg) { |
||||
|
// The PRI value is an integer number which calculates by the following metric:
|
||||
|
uint8_t priority = (8 * facility) + severity; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
// This is a unit8 instead of a char because that's what udp.write() wants
|
||||
|
uint8_t buffer[SYSLOG_MAX_PACKET_SIZE]; |
||||
|
int len = snprintf((char*)buffer, SYSLOG_MAX_PACKET_SIZE, "<%d>%s %s: %s", priority, hostname, SYSLOG_APP, msg); |
||||
|
//printf("syslog::log %s\n",mSyslogIP.toString().c_str());
|
||||
|
//printf("syslog::log %d %s\n",len,buffer);
|
||||
|
// Send the raw UDP packet
|
||||
|
mSyslogUdp.beginPacket(mSyslogIP, SYSLOG_PORT); |
||||
|
mSyslogUdp.write(buffer, len); |
||||
|
mSyslogUdp.endPacket(); |
||||
|
} |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#endif |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@ |
|||||
|
|
||||
|
#ifndef __SYSLOG_H__ |
||||
|
#define __SYSLOG_H__ |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#ifdef ESP8266 |
||||
|
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h> |
||||
|
#elif defined(ESP32) |
||||
|
#include <WiFi.h> |
||||
|
#endif |
||||
|
#include <WiFiUdp.h> |
||||
|
#include "../config/config.h" |
||||
|
#include "../config/settings.h" |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#ifdef ENABLE_SYSLOG |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#define SYSLOG_BUF_SIZE 255 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#define PRI_EMERGENCY 0 |
||||
|
#define PRI_ALERT 1 |
||||
|
#define PRI_CRITICAL 2 |
||||
|
#define PRI_ERROR 3 |
||||
|
#define PRI_WARNING 4 |
||||
|
#define PRI_NOTICE 5 |
||||
|
#define PRI_INFO 6 |
||||
|
#define PRI_DEBUG 7 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#define FAC_USER 1 |
||||
|
#define FAC_LOCAL0 16 |
||||
|
#define FAC_LOCAL1 17 |
||||
|
#define FAC_LOCAL2 18 |
||||
|
#define FAC_LOCAL3 19 |
||||
|
#define FAC_LOCAL4 20 |
||||
|
#define FAC_LOCAL5 21 |
||||
|
#define FAC_LOCAL6 22 |
||||
|
#define FAC_LOCAL7 23 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
class DbgSyslog { |
||||
|
public: |
||||
|
void setup (settings_t *config); |
||||
|
void syslogCb(String msg); |
||||
|
void log(const char *hostname, uint8_t facility, uint8_t severity, char* msg); |
||||
|
|
||||
|
private: |
||||
|
WiFiUDP mSyslogUdp; |
||||
|
IPAddress mSyslogIP; |
||||
|
settings_t *mConfig; |
||||
|
char mSyslogBuffer[SYSLOG_BUF_SIZE+1]; |
||||
|
uint16_t mSyslogBufFill = 0; |
||||
|
int mSyslogSeverity = PRI_NOTICE; |
||||
|
}; |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#endif /*ENABLE_SYSLOG*/ |
||||
|
|
||||
|
#endif /*__SYSLOG_H__*/ |
||||
Loading…
Reference in new issue